cheese hazard analysis
The hazard analysis critical control point system HACCP is a widely used tool in the food industry and recommended in the water safety plans WSP approach. The hazard analysis is a useful inexpensive and easy technique to determine the shelf-life of cottage cheese.
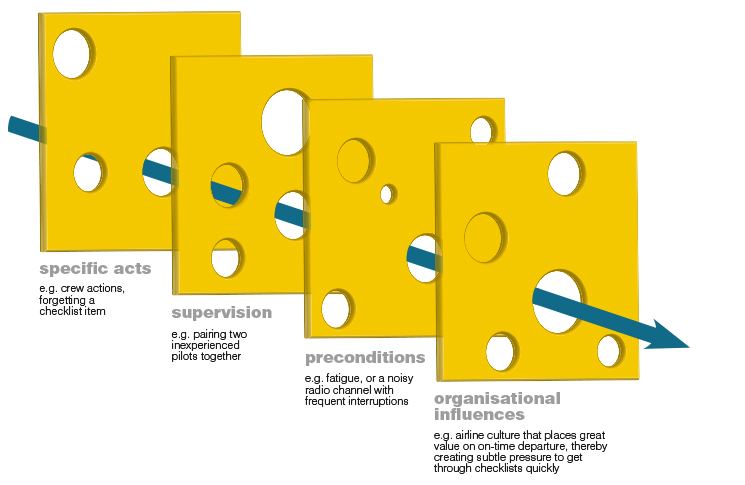
Safety In Mind Swiss Cheese And Bowties Flight Safety Australia
For a manufacturer this infonnation would be useful so that shelf-life can be la beled more accurately thus reducing waste and loss of.

. 33 at critical control point 1 ccp1 cheese pasteurisa- tion two types of hazards were identified. There was no dose-response relationship between cheese consumption and risk of all-cause mortality RR per 43 gday 103 95 CI. Secondly any ready-to-eat food exposed to the processing environment is a risk for Listeria.
Most common hazard associated with tree nuts. Our findings suggest that long-term cheese consumption was not associated with an increased risk of all-cause mortality. Brazil two cheese plants 13 10 Barancelli 2011.
Although the cheesemaking process for some cheeses will. 1 they were authorized by the Canary Health Service of The Autonomous Government of the Canaries to produce and sell cheese. To set up a specific HACCP plan for this small-scale cheese plant.
In 1993 the European union issued a food hygiene directive EU 1993 establishing a general requirement for all food products to adopt a risk based food safety management system with the principles of the internationally accepted system Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point HACCP recommended. All made fresh cheese. 1 microbiological introduction of pathogenic mi- croorganisms due to improper handling and sur- vival of microorganisms due to insufficient pas- teurisation time andor temperature and 2 chemical contamination with sanitation chemi- cal.
Cheese is generally considered a safe and nutritious food but foodborne illnesses linked to cheese consumption have occurred in many countries. Remove at least 1-inch around and below the mold spot. In this study a methodological.
17 of 243 noncontact surfaces Menendez. The key determinant for the safety of raw milk cheese is the microbiological quality of the raw milk. Any component of an organization is considered as a cheese slice of this model.
To document the HACCP plan in order to demonstrate the. 7 28 of non food contact surfaces in cheese plants. In a recent study on Monte Veronese cheese an Italian PDO semi- hard cheese made with raw milk Staphylococcus aureusnumbers in cheese were higher than the104CFU g-1limit in 78 of samples 1.
Mold requires oxygen to grow so tightly rewrap the remaining cheese. Staphylococcus aureuswas the most frequent pathogen associated with cheeses from raw or unspecified milk in food-borne disease. The results revealed that the highest contamination by Staph.
For each hazard the section details its nature its characteristics and. - Hazard analysis presented in appendix in order not to weigh on the operational part of the document. The ruling outlines updated and revised requirements for current good manufacturing practice for human food.
HAZARDS IN RAW MILK CHEESES. There are several programs used in UF white cheese pro-duction line. 3 they produced between 10 and 1000 L of milk per day.
This section details the main chemical physical and microbiological hazards that concern dairy products and lists the more relevant ones that are referred to in the other sections of the document. Keep the knife out of the mold itself so it will not contaminate other parts of the cheese. The concept of Hazard Analysis of Critical Control Points HACCP is a preventive structured systematic and documented approach to ensure food safety Bu-chanan 1990 Motarjemi Kaferstein Moy Miyagawa Miyagishima 1996.
Salmonella has caused numerous outbreaks related to nuts and nut butters. Escherichia coli Staphylococcus aureus Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella spp. Aureus 439 105cfumL was found in milk and the highest.
Buildings and facilities must be of sound construction and. Salmonella caused 17 illnesses in raw cashew cheese made by a West Sacramento CA small processor US. Once the distri bution is determined on the appropriate hazard plots an accurate idea of the shelf-life can be realized.
The 39 cheese farms that participated in this study fulfilled the following requirements. The microbiological status of 773 raw milk and cheese samples from the cheese farms was assessed by enumerating total viable counts and 4 pathogens. Several microbial risk assessments related to Listeria monocytogenes Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli infections causing cheese-related foodborne illnesses have been conducted.
The traditional inspection and quality procedure in order to prevent the hazards in the cheese product. If the block of cheese is large and molding is not extensive remove the mold to save the remaining cheese. Implementation of the Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point HACCP system.
11 of noncontact surfaces in eight NJ artisan cheese factories. To evaluate the current methods of analysis on hazards that appear during the processing and control procedures used in the plant. It is generally recognized that the production of cheeses with desirable organoleptic char-.
Further analysis was undertaken to determine if it was possible to apply the findings of the risk assessments to other cheeses which lie within the same moisture category. Management resource allocation efficient safety program operational support all are considered as a part of the cheese. The Preventive Controls For Human Food PCHF is one component of the legislation and can be found in 21 CFR 117 Current Good Manufacturing Practice Hazard Analysis and Risk Based Preventive Controls for Human Food HARPC.
The Swiss cheese model is a theoretical assumption that is used in risk management risk analysis and risk prevention before any accident. No significant publication bias was observed. 2 all operated food safety management HACCP.
It is generally recognized that the cheese production with desirable. Acta Scientiarum Polonorum Technologia Alimentaria 93 2010 335 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Development of UF white cheese HACCP plan 1.

A Swiss Cheese Model For Reducing Biases In User Research By Biswajeet Das Ux Collective

Critical Control Points In Haccp System Set Up In Cream Cheese Production Download Table

Pdf Implementation Of Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point To Feta And Manouri Cheese Production Lines Semantic Scholar

Hazard Analysis Of Cheese Processing Steps Download Table

How Swiss Cheese Can Save Our School Children By Freeman Marvin Medium

Pdf Implementation Of Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point To Feta And Manouri Cheese Production Lines Semantic Scholar

Swiss Cheese Model Safety Hazard Accident Traditional Culture Angle Text Png Pngegg

Hazard Analysis Of Cheese Processing Steps Download Table

Pdf Hazard Analysis Of Cheese Provided For Consumers In Hawassa Ethiopia

What S Swiss Cheese Got To Do With Root Cause Analysis
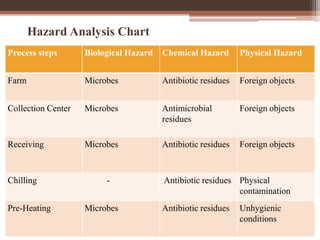
Haccp Implementation On Cheddar Cheese

Pdf Review On Hazard Analysis And Critical Control Point Haccp In The Dairy Product Cheese

Swiss Cheese And Safety Michigan Tech Research Blog

Pdf Implementation Of Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point To Feta And Manouri Cheese Production Lines Semantic Scholar

Critical Control Points In Haccp System Set Up In Cream Cheese Production Download Table


0 Response to "cheese hazard analysis"
Post a Comment